
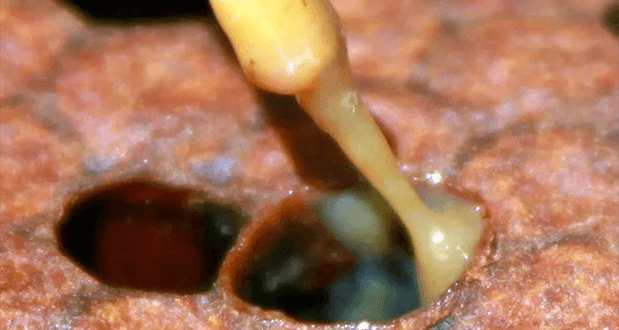
American Foulbrood is a highly contagious, fatal, and devastating disease that affects the developing honeybee larvae. The disease, caused by the bacteria Paenibacillus larvae, is considered the most deadly bacterial honeybee disease due its rapid spread and the limited treatment options available. P. larvae spores are resilient, surviving for years, and spreading through contaminated equipment, bees, or hive products. Infected larvae die after cell capping, turning into a gooey mass, later drying into a hard scale that releases more spores. The disease-causing bacteria is present in 50% of hives and can erupt at any time.
Dalan’s prophylactic and sustainable approach aims to decrease the risk of infections, saving not only hives, but protecting from revenue loss and excess costs.
According to estimates in the U.S. alone, lost annual revenue due to AFB and other diseases is estimated at $400 million and growing.
The Most Destructive Honey Bee Disease
Credit: Image by Margarita M. López-Uribe

The Only Safe Prophylactic Intervention
In the U.S., AFB outbreaks had previously been controlled with the routine use of antibiotics. However, heavy antibiotic usage has its own consequences, such as bacterial resistance and negative effects on overall hive health. In 2017, the FDA eliminated the prophylactic use of antibiotics, leaving the industry without an effective solution.
Dalan’s prophylactic and sustainable approach aims to decrease the risk of infections, saving not only hives, but protecting from revenue loss and excess costs.
Enter your information here to view the list of certified queen bee retailers near you.
Understanding AFB
American Foulbrood (AFB) exhibits distinct symptoms in bee brood, including:
- Irregular brood patterns
- Visibly affected cell cappings, which may appear sunken, dark, or greasy due to decomposing larvae.
- Perforated cappings from bees attempting to remove dead brood.
Larvae infected by AFB turn into a dark brown semi-liquid mass, and affected hives can emit a sulphurous odor. Advanced infection stages reveal darkened brood and a scale-like residue within cells, indicating severe larval decay.
Beekeepers should inspect their brood combs for American Foulbrood (AFB) symptoms twice per year, focusing on both strong and weak colonies. Inspections involve removing brood frames and examining them for:
- Irregular brood patterns
- Visibly affected cell cappings, which may appear sunken, dark, or greasy due to decomposing larvae.
- Perforated cappings from bees attempting to remove dead brood.
Early detection is crucial, as initial infections might only affect a few cells.
The “ropiness test” is recommended for cells showing AFB symptoms. The test involves inserting a matchstick into a suspect cell and pulling it out to observe the consistency of the contents. A ropy, dark-brown thread indicates possible AFB infection.
AFB spreads through beekeeper activities or bee behaviors, involving transfer of infected materials or robbing between hives. Avoid using honey or pollen from different colonies as feed unless it has been properly irradiated. It is also crucial to avoid using equipment from infected hives in healthy ones and to sterilize or destroy infected materials since AFB spores are highly resilient and can survive in the environment for over 50 years. As little as 6-10 spores can be enough to cause clinical AFB symptoms1.
AFB’s distribution is global, affecting honey bees worldwide.
The spread of AFB within a bee colony correlates with the quantity of spores and bee population; more spores lead to faster colony decline. However, effective AFB management relies on preventive beekeeping practices and immediate action upon outbreak detection to prevent further spread. These practices include:
- Hygienic Behavior – choosing bees that have been bred with genetic traits to detect and remove infected brood
- Effective Colony Management – this includes:
- Bi-annual brood comb inspections
- Replacing brood combs every 3-4 years to avoid them becoming bacteria reservoirs
- Minimizing hive material exchange
- Thoroughly cleaning tools and equipment after use in infected hives.
- Irradiation/elimination of infected spores if AFB is detected OR buring all hive components.
- Antibiotics – In some areas, antibiotics are used prophylactically to prevent AFB infection, but this is discouraged due to its ineffectiveness in spore eradication, potential for creating antibiotic-resistant strains, and negative effects on the honeybee microbiome.
Subscribe to our Newsletter
Get the latest in animal health and sustainability directly from Dalan. Our newsletter provides concise, essential updates and breakthroughs. Subscribe to stay ahead in sustainable solutions.
© 2024 Dalan Animal Health. All rights reserved.
